Mechanical Engineering Design Shigley Solution Manual
A machine (or mechanical device) is a mechanical structure that uses power to apply forces. In 1586 Flemish engineer Simon Stevin derived the mechanical advantage of the inclined. The classification of simple machines to provide a strategy for the design of new. Shigley (2003). Engineering Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design 8th Ed − Solution Manual By. The Instructor Solutions manual is available in PDF format for the following details, title, author and edition of the solutions manual you need to Advanced Accounting 10th ED ( Instructor's. Shigley's mechanical engineering design / Richard G. A complete online solutions manual organization system that allows.
Shigley’s Mechanical Engineering Design, Eighth Edition Budynas−Nisbett Shigley’s Mechanical Engineering Design, Eighth Edition Budynas−Nisbett Mechanical Engineering Copyright ©2006 by The McGraw−Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.Printed in the United States of America. Except as permitted under the United States Copyright Act of 1976, no part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, or stored in a database or retrieval system, without prior written permission of the publisher. This McGraw−Hill Primis text may include materials submitted to McGraw−Hill for publication by the instructor of this course. The instructor is solely responsible for the editorial content of such materials. This book was printed on recycled paper.
Shigleys Machine Design Solutions

Mechanical Engineering Contents Budynas−Nisbett. Shigley’s Mechanical Engineering Design, Eighth Edition Front Matter 1 Preface 1 List of Symbols 5 I. Basics 8 Introduction 8 1. Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Design 9 2. Materials 3 3. Load and Stress Analysis 72 4. Deflection and Stiffness 145 I.
Failure Prevention 208 Introduction 208 5. Failures Resulting from Static Loading 209 6. Fatigue Failure Resulting from Variable Loading 260 I.
Design of Mechanical Elements 349 Introduction 349 7. Shafts and Shaft Components 350 8. Screws, Fasteners, and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints 398 9. Welding, Bonding, and the Design of Permanent Joints 460 10.
Mechanical Springs 501 1. Rolling−Contact Bearings 550 12. Lubrication and Journal Bearings 597 13. Gears — General 652 14. Spur and Helical Gears 711 15. Bevel and Worm Gears 762 16. Clutches, Brakes, Couplings, and Flywheels 802 17. Mariner 8hp outboard motor owners manual.
Flexible Mechanical Elements 856 18. Power Transmission Case Study 909 IV. Analysis Tools 928 Introduction 928 19. Finite−Element Analysis 929 20. Statistical Considerations 952 Back Matter 978 Appendix A: Useful Tables 978 Appendix B: Answers to Selected Problems 1034 Index 1039 Budynas−Nisbett: Shigley’s Mechanical Engineering Design, Eighth Edition Front MatterPreface1© The McGraw−Hill Companies, 2008 Objectives This text is intended for students beginning the study of mechanical engineering design.
The focus is on blending fundamental development of concepts with practical specification of components. Students of this text should find that it inherently directs them into familiarity with both the basis for decisions and the standards of industrial components. For this reason, as students transition to practicing engineers, they will find that this text is indispensable as a reference text. The objectives of the text are to:.Cover the basics of machine design, including the design process, engineering mechanics and materials, failure prevention under static and variable loading, and characteristics of the principal types of mechanical elements.Offer a practical approach to the subject through a wide range of real-world applications and examples.Encourage readers to link design and analysis.Encourage readers to link fundamental concepts with practical component specification. New to This Edition This eighth edition contains the following significant enhancements:.New chapter on the Finite Element Method.In response to many requests from reviewers, this edition presents an introductory chapter on the finite element method. The goal of this chapter is to provide an overview of the terminology, method, capabilities, and applications of this tool in the design environment.New transmission case study.The traditional separation of topics into chapters sometimes leaves students at a loss when it comes time to integrate dependent topics in a larger design process.
A comprehensive case study is incorporated through standalone example problems in multiple chapters, then culminated with a new chapter that discusses and demonstrates the integration of the parts into a complete design process. Example problems relevant to the case study are presented on engineering paper background to quickly identify them as part of the case study.Revised and expanded coverage of shaft design.Complementing the new transmission case study is a significantly revised and expanded chapter focusing on issues relevant to shaft design. The motivating goal is to provide a meaningful presentation that allows a new designer to progress through the entire shaft design process – from general shaft layout to specifying dimensions. The chapter has been moved to immediately follow the fatigue chapter, providing an opportunity to seamlessly transition from the fatigue coverage to its application in the design of shafts.Availability of information to complete the details of a design.Additional focus is placed on ensuring the designer can carry the process through to completion.
Preface Budynas−Nisbett: Shigley’s Mechanical Engineering Design, Eighth Edition Front MatterPreface2© The McGraw−Hill Companies, 2008 By assigning larger design problems in class, the authors have identified where the students lack details. For example, information is now provided for such details as specifying keys to transmit torque, stress concentration factors for keyways and retaining ring grooves, and allowable deflections for gears and bearings. The use of internet catalogs and engineering component search engines is emphasized to obtain current component specifications.Streamlining of presentation.Coverage of material continues to be streamlined to focus on presenting straightforward concept development and a clear design procedure for student designers. Content Changes and Reorganization A new Part 4: Analysis Toolshas been added at the end of the book to include the new chapter on finite elements and the chapter on statistical considerations. Based on a survey of instructors, the consensus was to move these chapters to the end of the book where they are available to those instructors wishing to use them.
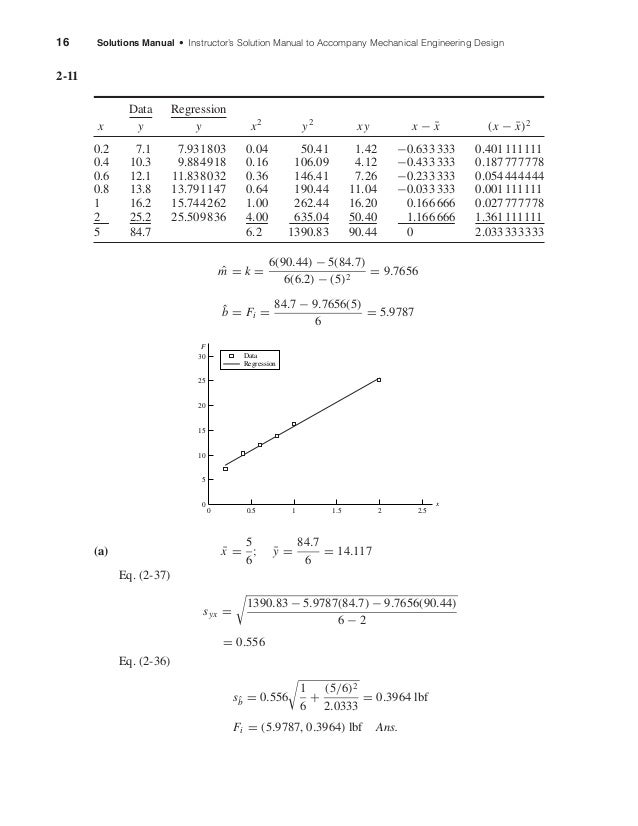
Moving the statistical chapter from its former location causes the renumbering of the former chapters 2 through 7. Since the shaft chapter has been moved to immediately follow the fatigue chapter, the component chapters (Chapters 8 through 17) maintain their same numbering.
The new organization, along with brief comments on content changes, is given below: Part 1: Basics Part 1 provides a logical and unified introduction to the background material needed for machine design. The chapters in Part 1 have received a thorough cleanup to streamline and sharpen the focus, and eliminate clutter.Chapter 1, Introduction.Some outdated and unnecessary material has been removed. A new section on problem specification introduces the transmission case study.Chapter 2, Materials.New material is included on selecting materials in a design process. The Ashby charts are included and referenced as a design tool.Chapter 3, Load and Stress Analysis.Several sections have been rewritten to improve clarity. Bending in two planes is specifically addressed, along with an example problem.Chapter 4, Deflection and Stiffness.Several sections have been rewritten to improve clarity. A new example problem for deflection of a stepped shaft is included. A new section is included on elastic stability of structural members in compression.
Part 2: Failure Prevention (Parte 1 de 14).